Creating a mileage matrix grid is easy enough if you only have a few addresses. But what if you have dozens of addresses? Enter Python, the GoogleMaps API, and the popular data-science library, Pandas.
What we need to begin with is a dictionary of addresses. For each address, we want the distance from that address to all other addresses in the dictionary, including itself. Our end result will be a dataframe that we can write to Excel and format and style as we wish.
Let's start by importing the necessary packages we'll need. You'll most likely need to pip install googlemaps and pandas
import googlemaps
import math, time
import datetime
import pandas as pd
Let's create our dictionary of addresses, where the key is the simple name of the address which wil be displayed in the rows and columns of the dataframe, and the value is the street address.
addys = {
'White House':'1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW, Washington, DC 20500',
'Empire St. Bldg': 'Empire State Building':'350 5th Ave, New York, NY 10118',
'Niagara Falls':'Niagara Falls, NY 14303',
'PPG Arena':'1001 Fifth Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15219'
}
Create the googlemaps object:
gmaps = googlemaps.Client(key='YOUR_OWN_KEY')
Create an empty array that will be fed the distance (in meters)
addyMeters = []
And then loop through all of our values/addresses in addys, append addyMeters so that it results in a two-dimensional array.
for k, origin in addys.items():
addyMeters.append([])
Loop through addys again to call the Google MAPS api for each destination address to calculate, and call the google MAP's distance_matrix method on the origin and destination addresses and assign it to the variable directions.
for x, destination in addys:
directions = gmaps.distance_matrix(origin, destination)
The distance_matrix method returns JSON data stored in our directions variable as a Python dictionary where we can access nested values by slicing.
directions = {
'destination_addresses': ['1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW, Washington, DC 20500, USA'],
'origin_addresses': ['350 5th Ave, New York, NY 10118, USA'],
'rows': [{'elements': [{'distance': {'text': '372 km',
'value': 371866}, 'duration': {'text': '3 hours 54 mins',
'value': 14037}, 'status': 'OK'}]}],
'status': 'OK',
}
What we want for our mileage matrix is the value in the 'distance' rows. This value is in meters, so we have to convert it to miles, where one mile == 0.000621371 meters. So we access the value in meters and multiply it by 0.000621371 and use math.floor to give us the nearest integer.
try:
meters = math.floor(directions['rows'][0]['elements'][0]['distance']['value']*0.000621371)
addyMeters[-1].append(meters)
except:
addyMeters[-1].append("Error with {0} and {1}".format(origin,destination))
time.sleep(3)
To recap: we have our addys list which includes all of the addresses and now our two-dimensional array (list within a list) with all of the distances in miles.
We can now use Pandas to turn this into an easy to view data frame, and write it to an Excel file using Panda's ExcelWriter and the xlsxwriter engine.
df = pd.DataFrame(addyMeters, columns=addys, index=addys)
writer = pd.ExcelWriter('mileagematrix.xlsx', engine='xlsxwriter')
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Sheet1')
writer.save()
Here is the result!
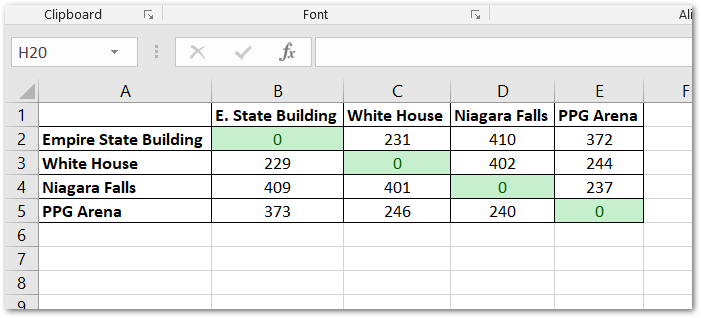
Things to consider: Google Maps API has pretty strict usage quotas. If you have dozens or hundreds of addresses, you may want to look at alternative solutions or use time.sleep() to slow down your requests to the API.
Comments
comments powered by Disqus